The United States, a major player in the global strawberry market, produces approximately 20% of the world’s strawberries. With California and Florida contributing 89% and 10% of the national yield respectively, American growers are turning to innovative methods to maintain their competitive edge. As competition intensifies from neighboring countries, the use of protected structures like high tunnels, greenhouses, and indoor farms is becoming increasingly prevalent. These structures not only extend the growing season but also enhance yields, particularly in regions with non-temperate climates.
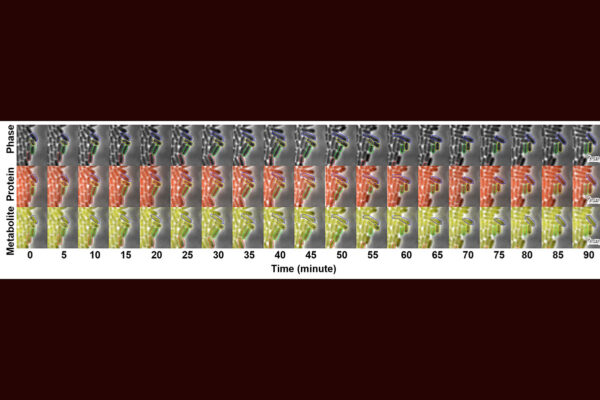
Light intensity is a critical factor in plant development, affecting photosynthesis, rooting success, and overall plant vigor. While numerous studies have explored the use of LED lighting during propagation, the specific impact of photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) on the rooting of vegetative plant material, such as strawberry runner tips, remains under-researched. Traditionally, growers maintain low PPFDs (≤70 µmol·m‒2·s‒1) to minimize water loss until active root growth is established.
Research Insights on Light Intensity and Plant Development
Recent research delves into how varying PPFD levels influence the physiological responses of strawberry runner tips, focusing on rooting efficiency, leaf development, and overall productivity. The findings reveal that manipulating light intensity significantly impacts the establishment and quality of young plants, paving the way for improved propagation practices.
Higher PPFD levels enhance biomass and rooting of indoor-propagated strawberry runner tips but can also induce radiation stress, leading to increased shoot mortality, reduced chlorophyll, and lower gas exchange.
While higher PPFDs may expedite the rooting process, they necessitate additional strategies, such as selecting runner tips with larger crowns, to optimize final plant growth and yield. This nuanced approach to light management could revolutionize indoor propagation strategies, enabling growers to produce more uniform and resilient transplants that adapt better to field or greenhouse conditions.
Implications for Controlled-Environment Agriculture
These findings underscore the potential for advancements in controlled-environment agriculture, contributing to more efficient and sustainable strawberry production. By refining indoor propagation techniques, growers can ensure a consistent supply of high-quality transplants, bolstering their competitive position in the global market.
Dr. Góemez, an Associate Professor of Controlled Environment Agriculture at Purdue University, emphasizes the importance of such research. Her program focuses on evaluating new crops and innovative production systems within the controlled environment horticulture industry.
“By understanding the intricate balance of light intensity and plant development, we can significantly enhance the efficiency and sustainability of strawberry production,” Dr. Góemez states.
The Role of Professional Societies in Horticultural Advancements
The American Society for Horticultural Science (ASHS), established in 1903, plays a pivotal role in promoting scientific research and education in horticulture. Recognized globally as a leading professional society, ASHS is dedicated to fostering national and international interest in all branches of horticulture.
With thousands of members worldwide, ASHS represents a diverse cross-section of the horticultural community, including scientists, educators, students, landscape managers, government officials, extension agents, and industry professionals. Their collective focus spans the entire horticultural spectrum, from breeding and propagation to marketing and use of horticultural plants and products.
For more detailed insights into this research, the full study is available in the ASHS HortScience electronic journal. Visit here to access the complete article.
As the horticultural industry continues to evolve, the integration of scientific advancements with traditional practices will be crucial in meeting the challenges of modern agriculture. The ongoing research and development efforts by organizations like ASHS ensure that growers have the tools and knowledge necessary to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.