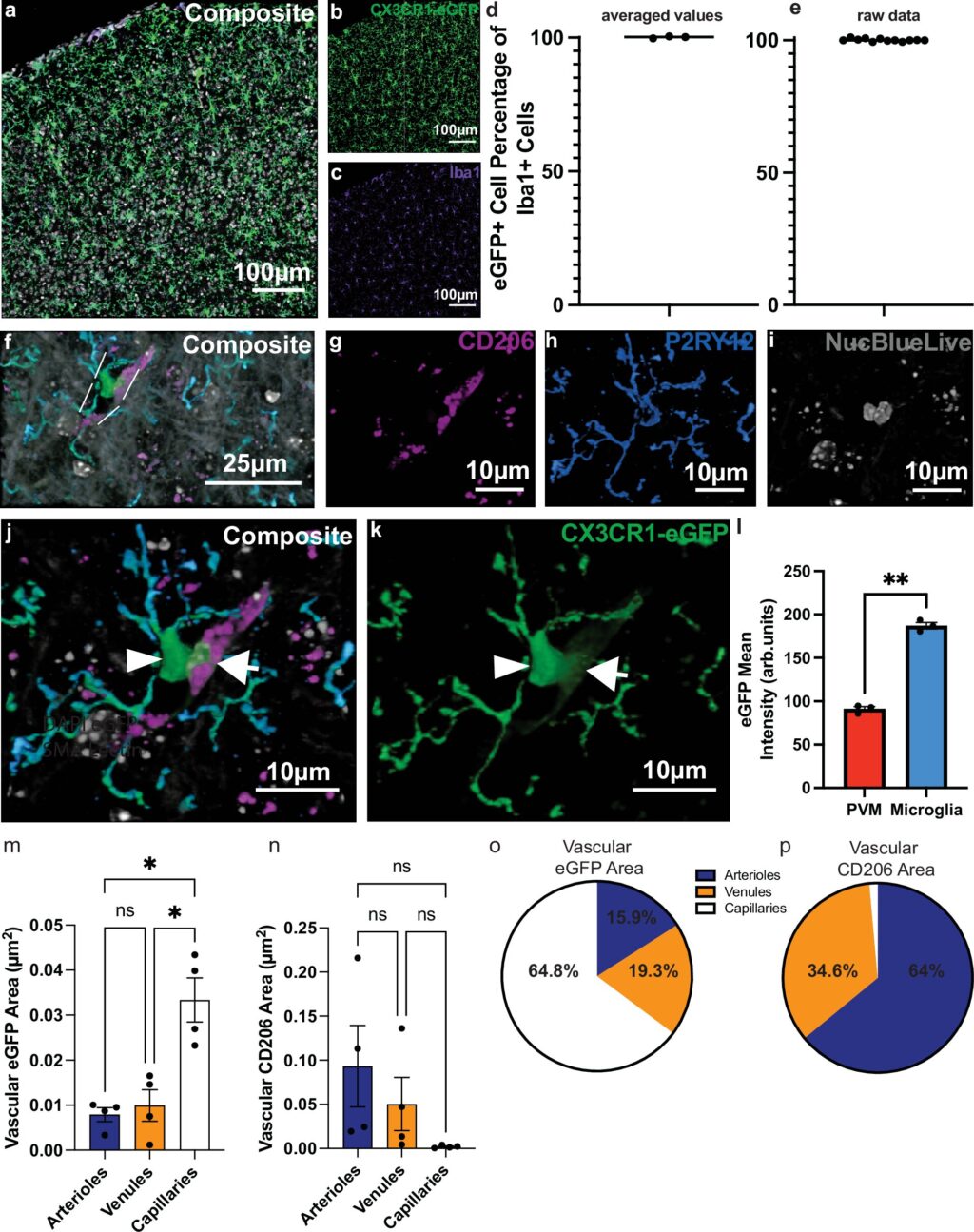
In a groundbreaking study, researchers from the University of Virginia School of Medicine have uncovered a novel approach to combating Alzheimer’s disease by enhancing blood flow to the brain. This discovery, led by Dr. Ukpong B. Eyo and his team, highlights the critical role of immune cells known as microglia in regulating the brain’s blood supply. Published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, the findings suggest that targeting these cells could offer new therapeutic avenues not only for Alzheimer’s but also for other neurodegenerative diseases like vascular dementia and Parkinson’s.
Microglia, which are pivotal in maintaining the health of the brain’s capillaries, have been shown to influence how well these tiny blood vessels deliver essential nutrients and oxygen. The study reveals that dysfunction in microglia may contribute to the deterioration of brain health, and rectifying these dysfunctions could potentially halt or reverse the progression of memory-related diseases.
The Role of Microglia in Brain Health
Our brains, despite constituting only 2% of our body weight, consume a staggering 20% of our total energy. This high demand is met by an extensive network of blood vessels, spanning approximately 400 miles, that branch into minute capillaries. The proper functioning of these vessels is crucial for maintaining cognitive health.
Previous research has established that myeloid cells, a category to which microglia belong, are involved in managing blood flow and oxygenation in the brain. However, Dr. Eyo’s team sought to pinpoint which specific cells were responsible for these functions and what consequences arose when they malfunctioned.
“For some time now, microglia have been suggested to play important roles in regulating vessel function. With this study, we have provided the most definitive evidence that they do regulate blood flow to the brain,” stated Dr. Eyo, emphasizing the significance of their findings.
Implications for Alzheimer’s and Beyond
The researchers discovered that microglia are essential for maintaining the “tone” of capillaries, which affects their ability to transport blood effectively. When microglia were removed, the capillaries narrowed, impairing blood flow. Conversely, restoring microglia improved capillary function.
Dr. William A. Mills III, the study’s first author, noted, “The microglial enzyme identified in this study has been targeted heretofore in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, albeit with mixed results. Our study suggests that these therapeutics would have maximal benefit if prescribed according to the therapeutic window of microglia in Alzheimer’s.”
This insight opens the door to more effective treatment strategies, potentially leading to significant advancements in how Alzheimer’s and similar diseases are managed. The research team is now focused on understanding the complex interactions between microglia and other brain cells, as well as the timing of microglial interventions.
Future Research Directions
The study has laid the groundwork for further exploration into the role of microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Dr. Eyo and his colleagues are keen to investigate whether microglia operate independently or in conjunction with other brain cells to regulate capillary function. They are also interested in determining when microglia begin to play their role during development and whether this role is significant in neurodevelopmental disorders.
“Now that we have identified a novel role for microglia in blood vessel structure and function, we are poised to examine how this enzyme and microglial functions change, and to subsequently develop therapies to reduce these changes during neurodegenerative diseases broadly and in Alzheimer’s disease especially,” Dr. Eyo explained.
The research team, comprising experts such as Niesha A. Savory, Aida Oryza Lopez-Ortiz, and others, is committed to advancing our understanding of microglia and their potential to rejuvenate blood flow in the brain. Their ongoing work promises to shed light on critical questions that could transform the landscape of neurological treatment.
As the scientific community continues to unravel the complexities of the brain, discoveries like this underscore the importance of innovative research in tackling some of the most challenging diseases of our time. The potential to enhance brain health by targeting microglia offers hope for millions affected by Alzheimer’s and related disorders.







