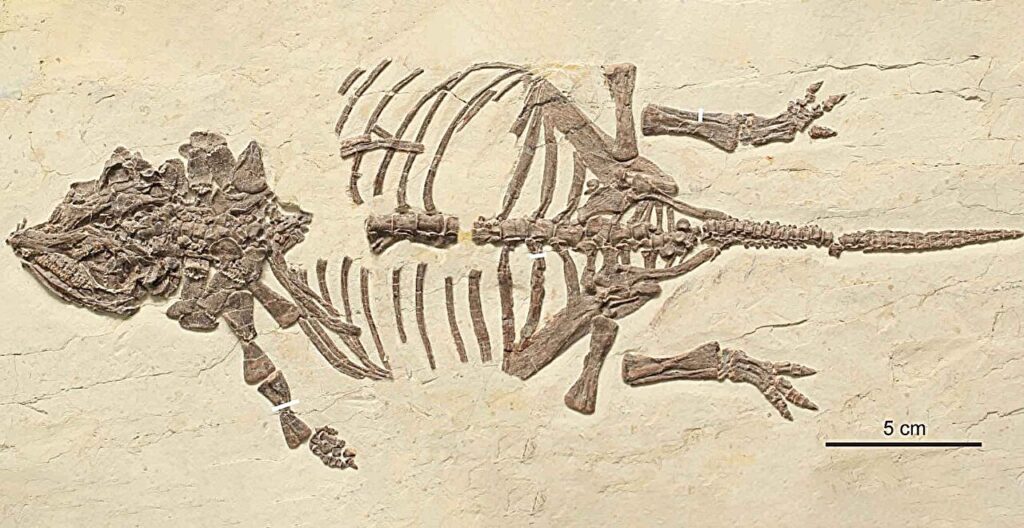
The mystery surrounding dozens of small dinosaur fossils in China has finally been unraveled. What were once thought to be miniature armored dinosaurs are now identified as baby ankylosaurs, providing scientists with fresh insights into the development of these remarkable creatures. This revelation comes from new research published in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
For over two decades, fossils belonging to a dinosaur species called Liaoningosaurus paradoxus have puzzled researchers. First described in 2001, these dinosaurs were initially classified as a type of armored dinosaur known as ankylosaurs. However, the fossils, all measuring less than 40 centimeters, were unusually small compared to the typical adult ankylosaurs that can grow up to three meters or more.
Revisiting Old Theories
In the absence of larger specimens, some scientists speculated that Liaoningosaurus might be the first known miniature ankylosaur, while others suggested they could be semi-aquatic. However, the latest study has overturned these theories, revealing that these tiny reptiles are likely juvenile ankylosaurs. One fossil even exhibited signs of having recently hatched, making it the youngest ankylosaur ever discovered.
“Liaoningosaurus has caused a lot of debate because there is a lot we don’t know about this species and we haven’t managed to identify an adult,” said Professor Paul Barrett, a co-author of the study. “But our research confirms that these are baby dinosaurs rather than small adults. Fossils of young ankylosaurs are rare, so there is a lot that these remains can tell us about the early development of armored dinosaurs.”
Understanding the Youthful Fossils
Determining the age of the Liaoningosaurus fossils required a detailed examination of their bone structure. Bone tissue contains growth lines, similar to tree rings, with each line representing a year of life. The number and spacing of these lines can reveal the age and growth rate of the individual.
Researchers analyzed bone samples from two Liaoningosaurus fossils, one being the largest specimen found and the other among the smallest. The absence of growth lines in both specimens indicated they were less than a year old. The bone microstructure of the smaller specimen also matched that of other dinosaurs in early development stages.
“The smaller fossil showed characteristics that we can see in other newborn dinosaurs, such as the presence of a hatching line,” Professor Barrett explained. “This is a small, ring-like feature in the bone that is laid down at the time the animal hatches from the egg. So, we can say that this individual had very recently hatched at the time of its death, which would make it the first hatchling ankylosaur we’ve ever discovered.”
The Significance of Liaoningosaurus
All known Liaoningosaurus specimens originate from Liaoning Province in northeastern China, a region renowned for its Cretaceous Period fossils, dating back 145 to 66 million years. This area has yielded many remarkable finds, including feathered dinosaurs like Microraptor and Sinornithosaurus.
The preservation of these fossils owes much to the region’s ancient shallow lakes and volcanic activity, which created ideal conditions for fossilization. Despite the lack of adult specimens, the discovery of these young ankylosaurs offers a rare glimpse into the early development of armored dinosaurs.
Typically, young ankylosaurs are found without the distinctive armor seen in adults, leading some researchers to propose that armor develops over time. However, Liaoningosaurus fossils show that some armor was present early in life.
“As we have found so few fossil babies, Liaoningosaurus is really the only good window we have into what ankylosaurs are like just after they hatch,” Barrett noted. “The Liaoningosaurus fossils had already developed some armor. Now that we know they are babies and not miniature adults, we can say that these kinds of features came in quite early during the animal’s growth.”
Looking Forward
The discovery of baby ankylosaurs in China not only solves a long-standing paleontological puzzle but also opens new avenues for understanding dinosaur development. Finding an adult Liaoningosaurus would further enhance our knowledge, allowing scientists to compare developmental stages within the species.
As researchers continue to explore the rich fossil beds of Liaoning Province, each new find holds the potential to reshape our understanding of the ancient world and the creatures that once roamed it. The study of these baby ankylosaurs is a testament to the ever-evolving nature of paleontological research and its ability to surprise and enlighten.







