The United Kingdom is witnessing a demographic shift as nearly one-fifth of its population is now aged 65 or older. This trend underscores the importance of addressing modifiable risk factors such as nutrition, which can significantly impact the aging process and the prevalence of chronic diseases. A new initiative aims to tackle this issue by developing a nutrition-focused digital tool for older adults.
Malnutrition, particularly undernutrition, affects approximately 1.3 million people over the age of 65 in the UK, with the vast majority living in the community. The prevention of malnutrition is crucial as it can exacerbate physical decline and frailty. In 2020, a Priority Setting Partnership identified early intervention in vulnerable groups as the top research priority for preventing malnutrition.
Innovative Digital Solutions for Nutrition
Digital technology is increasingly seen as a complement to traditional clinical approaches, offering the potential for greater efficiency and wider reach. The psychological literature suggests that behavior change, especially in older adults, is challenging due to long-established habits. However, digital tools that incorporate behavior change theories can effectively encourage positive lifestyle changes by considering social, emotional, and cognitive factors.
The “Keep on Keep up” (KOKU) digital tool, which provides strength and balance exercises, is now being expanded to include a nutrition game aimed at educating older adults about healthy eating in line with UK dietary guidelines. This initiative follows the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) guidelines to ensure a person-centered approach.
Development Process: A Collaborative Effort
The development of the nutrition game involved a three-phase process, beginning with focus groups to gather insights from older adults. These discussions revealed that physiological aging and psychosocial factors like retirement and bereavement significantly influence dietary behaviors. Participants expressed a desire for personalized dietary interventions that consider their preferences and ease of preparation.
“I try to cook by myself, because then I know what’s going in it,” said one participant, highlighting the importance of home cooking over processed foods.
The second phase involved designing the nutrition game through an agile design sprint, which encouraged collaboration and innovation. Researchers and designers worked together to create engaging mini-games that educate users about nutrition and encourage healthier eating habits.
Testing and Feedback: Ensuring Usability
The final phase of development included initial application testing with participants from the focus groups. Users tested the beta version of the app, providing feedback on its usability and educational content. The System Usability Scale (SUS) was used to evaluate the app, with results indicating excellent usability.
The median SUS score was 87.5, suggesting that the intervention had excellent usability.
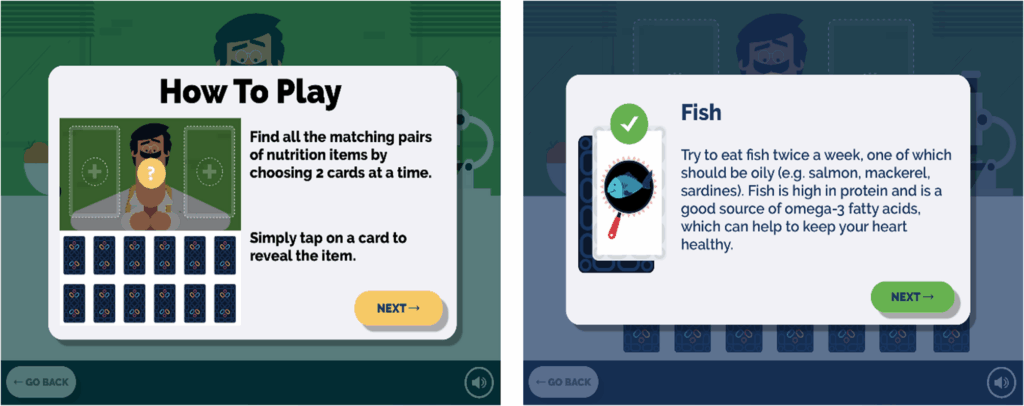
Feedback from users was generally positive, with suggestions for improvements being incorporated into the final design. The game, which includes a matching pairs card game, aims to educate users about the importance of consuming high-quality protein and other dietary guidelines.
Addressing Barriers and Enhancing Engagement
The study identified several barriers to technology use among older adults, including a lack of knowledge and confidence. However, many participants expressed a willingness to learn with the appropriate support. This highlights the importance of involving users in the design process to ensure accessibility and relevance.
“Well, I think I would like to learn because I’ve got to change my attitude to it and accept that it’s here to stay,” remarked one participant.
The use of gamification in the digital tool is expected to increase engagement by making the learning process more enjoyable and competitive. This approach aligns with established behavior change techniques and is likely to promote healthy behaviors through goal setting and feedback.
Future Implications and Research
The development of the KOKU-Nut digital tool represents a significant step forward in addressing malnutrition among older adults in the UK. By incorporating user feedback and evidence-based guidelines, the tool aims to improve dietary intake and quality of life for this population.
Future research should explore the long-term impact of the digital platform on health indicators and quality of life. Additionally, efforts should be made to engage a more diverse group of participants to enhance the generalizability of findings.
This person-centered approach to digital health interventions demonstrates the potential for technology to support older adults in maintaining healthy lifestyles, ultimately contributing to a longer, disability-free life.







