Wood remains the predominant material used in the construction of single-family homes across the United States. However, its limitations, particularly in the face of extreme weather events, are prompting a reevaluation of building materials. Concrete, with its resilience and affordability, is emerging as a viable alternative for the future of American housing.
Wood construction, while historically significant, is not engineered for long-term durability. This has become increasingly evident as climate change intensifies the frequency and severity of natural disasters. In response, experts are advocating for mass-produced concrete homes, leveraging innovations in the precast concrete industry to meet modern housing demands.
The Historical Dominance of Wood
Wood has been the cornerstone of American homebuilding since the earliest European settlers utilized native timber to construct shelters. The iconic log cabin, built from large tree trunks, became a symbol of early American architecture. The 1830s saw a shift with the introduction of balloon framing, which used standardized lumber and nails, making construction more accessible and economical.
By the early 20th century, platform framing had evolved, allowing each floor to be built as a separate platform, further simplifying construction. This method solidified wood’s place in the American housing market. Today, over 90% of new homes in the U.S. rely on wood framing due to its affordability and the familiarity of contractors with wood construction techniques.
However, wood’s vulnerabilities are significant. It is susceptible to fire, water damage, termites, mold, and structural deterioration, particularly in humid or poorly ventilated environments. These limitations underscore the need for more resilient building materials.
The Advantages of Concrete
Concrete has revolutionized architecture and engineering, offering unmatched strength and durability. It is low-cost, low-maintenance, and possesses high thermal mass properties, which can reduce heating and cooling costs. Concrete structures are resistant to a wide range of hazards, including fire, flooding, earthquakes, and severe weather.
Despite these benefits, concrete homes remain rare in the U.S., primarily due to the labor-intensive and costly cast-in-place construction method. This technique involves forming and pouring concrete on-site, which is both time-consuming and wasteful. The high labor costs in the U.S. further deter the use of concrete for single-family homes.
“Concrete’s durability and long service life often offset its environmental costs, making it a sustainable choice for long-term construction.”
Innovations in Precast Concrete
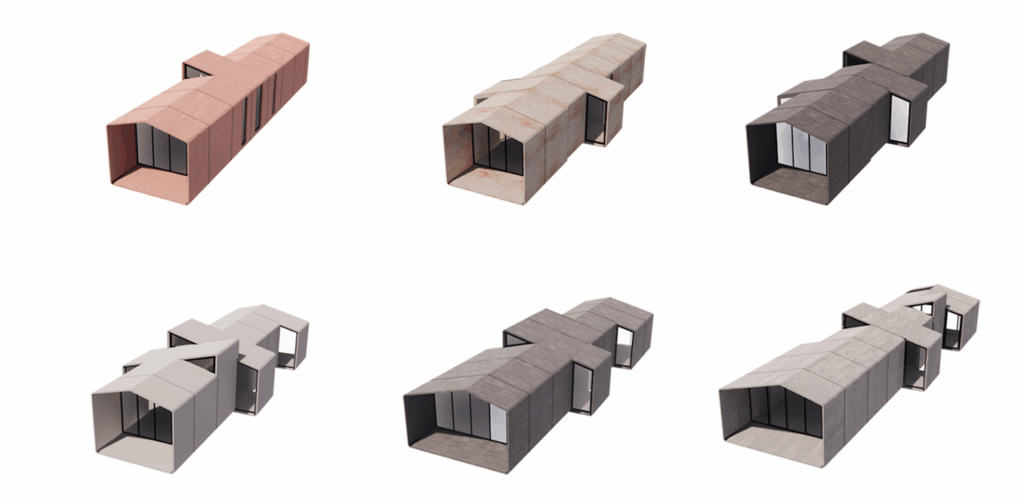
Precast concrete presents a promising alternative to traditional methods. Manufactured off-site under controlled conditions, precast systems improve quality while reducing waste and labor. The CRETE House, a prototype developed in 2017, demonstrated the potential of precast concrete homes. Using ultra-high-performance concrete, the structure was tested against extreme conditions, proving its resilience.
Building on this success, the Compact House was designed as an affordable, resilient housing solution. Its modular, precast concrete system allows for rapid assembly and reduced costs. The precast rings can be transported and assembled in a single day, making mass production feasible and competitive with traditional wood-framed homes.
“The precast concrete homes are designed to last over 100 years, significantly reducing utility bills, maintenance expenses, and insurance premiums.”
Challenges and Opportunities
While precast concrete offers numerous benefits, challenges remain. Transportation costs and size limitations of precast components can be significant. However, the existing infrastructure for precast concrete, used in commercial buildings and infrastructure projects, provides a foundation for expanding its use in residential construction.
Alternative concrete construction methods, such as concrete masonry units and insulated concrete forms, also offer potential solutions. However, these methods require more on-site labor compared to the modular precast approach.
Precast concrete homes represent a shift towards long-term value in housing, prioritizing resilience, efficiency, and equity. As the housing crisis continues, these innovations could redefine the future of affordable housing in the U.S.
This article is part of a series exploring solutions to the housing crisis, highlighting the role of innovative construction methods in creating sustainable, resilient communities.







