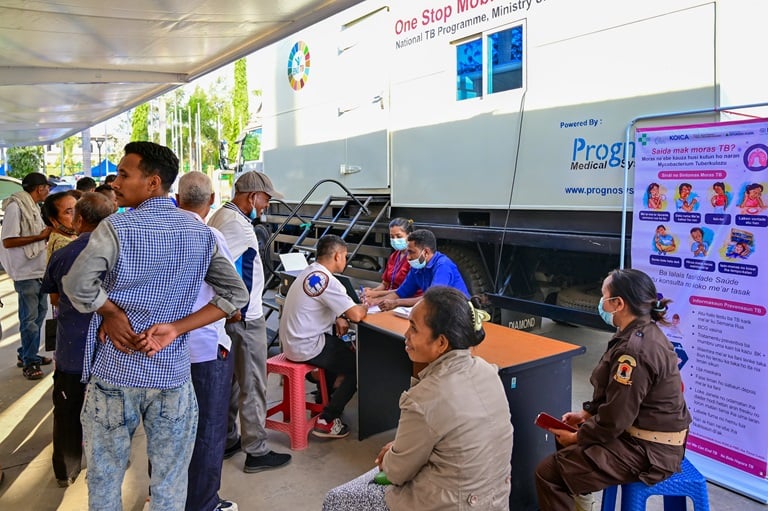
The World Health Organization (WHO) has unveiled updated Target Product Profiles (TPPs) for tuberculosis (TB) screening tests, aiming to enhance the development and deployment of new diagnostic tools. Released this week, these guidelines outline the essential characteristics and requirements for systematic TB screening and active case finding, crucial steps in combating the global TB epidemic.
Originally introduced in 2014, the WHO’s TPPs were designed to stimulate innovation in TB diagnostics, addressing the need for early detection tools that could identify cases often missed or delayed. Over the past decade, significant technological advancements have emerged, including portable digital radiographic equipment and AI-driven computer-aided detection software for automated chest X-ray interpretation. Despite these innovations, challenges persist in scaling up screening efforts to bridge the detection gap and reduce the global TB burden. Chief among these challenges is the need for cost-effective and highly accurate screening tools.
Advancements and Persistent Challenges
The updated 2025 TPPs offer technology-agnostic guidance, accommodating various approaches to TB screening. They identify three types of screening tools that may be effective in diverse settings and situations. Developed through extensive consultations with global experts, these TPPs are informed by models evaluating the performance and cost-effectiveness of novel tests.
Dr. Tereza Kasaeva, Director of the WHO Department for HIV, Tuberculosis, Hepatitis, and Sexually Transmitted Infections, emphasized the importance of accessible screening tools. “The global community needs tools to screen and detect TB which are better and more accessible in hard-to-reach settings,” she stated. “The new WHO TPPs will inform manufacturers about the features that these new tests should have if they are to address the needs of the TB community and achieve the ambitious global commitments for TB detection and reduction of TB incidence and deaths.”
Historical Context and Technological Progress
Since the first TPPs were published, there has been a concerted effort to leverage technological advancements in the fight against TB. The introduction of portable digital radiography and AI-enhanced diagnostics marks a significant leap forward. These tools have the potential to revolutionize TB screening, particularly in resource-limited settings where traditional methods fall short.
However, the path to widespread implementation is fraught with obstacles. The cost of deploying these technologies on a large scale remains prohibitive for many low-income countries, where the TB burden is often highest. Moreover, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of these tools in diverse environments is a critical concern that must be addressed to maximize their impact.
Future Implications and Global Health Goals
The updated WHO guidelines represent a strategic move to align TB screening efforts with global health objectives. By providing a clear framework for the development of new diagnostic tools, the TPPs aim to spur innovation and facilitate the creation of tests that are both effective and accessible.
Looking ahead, the successful implementation of these guidelines could significantly enhance TB detection rates, contributing to the broader goal of reducing TB incidence and mortality worldwide. As countries strive to meet the targets set by the WHO’s End TB Strategy, the development and deployment of advanced screening tools will be pivotal in achieving these ambitions.
In conclusion, the WHO’s updated TPPs for TB screening tests underscore the urgent need for continued innovation and collaboration in the global fight against tuberculosis. By setting clear standards and fostering technological advancements, these guidelines pave the way for a future where TB is detected and treated more effectively, ultimately saving lives and improving public health outcomes.