Chiba, Japan, January 12, 2026—A groundbreaking study from Japan’s National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology (QST) has placed quantum technologies at the forefront of life sciences innovation. The research, published in the journal ACS Nano on December 18, 2025, outlines the potential societal benefits of quantum advancements, including earlier disease detection, accelerated drug development, and novel approaches to clean energy.
By integrating innovations in sensing, imaging, and quantum biology, the authors of the study argue that quantum life science—an emerging discipline pioneered by QST—is poised to transition from specialized facilities to widespread applications across various fields.
Quantum Technologies in Life Sciences
The study presents a comprehensive roadmap with three key pillars demonstrating how new quantum technologies can revolutionize our understanding of life and leverage quantum effects within biological systems.
Nanoscale Quantum Biosensors
Among the highlighted technologies are nanoscale quantum biosensors, particularly fluorescent nanodiamonds hosting nitrogen-vacancy centers. These sensors can read out temperature, pH, and magnetic and electric fields inside living cells. With the ability to control and read electron spins optically, these biocompatible sensors offer real-time insights into cellular microenvironments that conventional tools cannot capture.
Potential applications include monitoring patient cell responses to therapies and guiding regenerative medicine. According to Dr. Hiroshi Yukawa, Project Director at the Institute for Quantum Life Science (iQLS), QST, “Our goal is to make quantum tools useful where it matters most—at the bedside and in the lab.”
Advancements in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
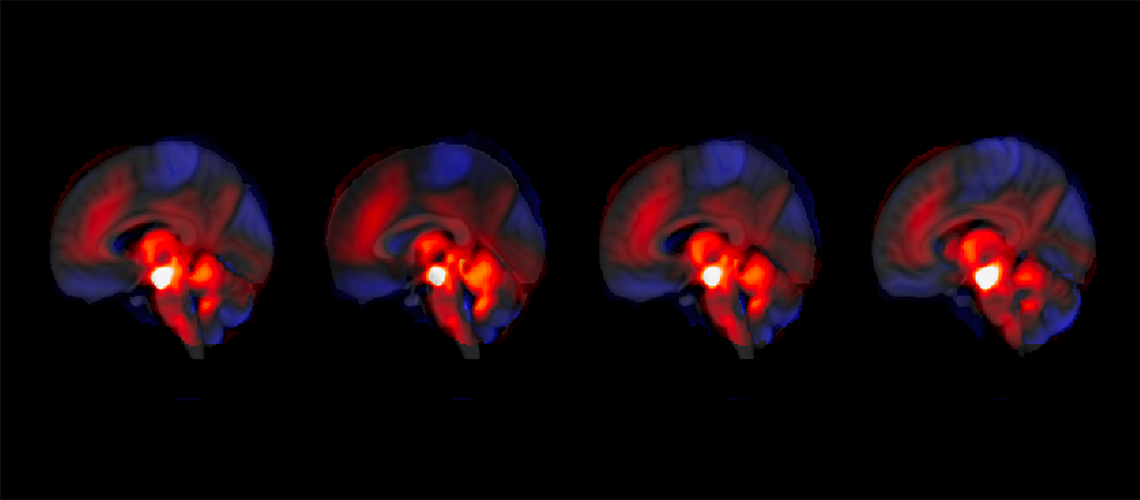
Another significant development is hyperpolarized magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), which amplify inherently weak magnetic resonance signals by more than 10,000-fold. This enhancement enables direct, time-resolved imaging of metabolism deep within tissues.
This approach is already providing insights into tumor metabolism and holds promise for real-time metabolic tracking with emerging probes and cost-effective polarization methods, paving the way for routine clinical use.
Quantum Biology and Biomimetic Innovations
Quantum biology offers engineering cues from nature, inspiring the creation of biomimetic sensors and catalysts. By unraveling mechanisms such as high-efficiency energy transfer in photosynthesis and quantum tunneling in enzyme reactions, researchers aim to design systems for clean energy, including oxygen-tolerant hydrogen production for fuel cells.
“We envision wearable devices equipped with diamond-based quantum sensors that can monitor temperature and chemical markers in real time—without invasive tests—transforming cancer diagnostics, brain disorder studies, regenerative medicine, and aging research,” says Dr. Yoshinobu Baba, Director General of iQLS.
Implications for Healthcare and Industry
The establishment of iQLS, the world’s first dedicated institute for quantum life science, underscores QST’s commitment to advancing this field. The authors emphasize that progress requires more than technological breakthroughs; it demands significant investment in human capital. Training the next generation of specialists is crucial to accelerating the transition from research labs to real-world applications in healthcare and industry.
Dr. Hidetoshi Kono, Deputy Director General of iQLS, highlights the broader vision: “Beyond elucidating the quantum phenomena occurring in our bodies, our vision is to make quantum life science part of everyday healthcare by bringing quantum tools from the lab to the bedside.”
Looking Ahead
The announcement comes as global interest in quantum technologies continues to grow, with numerous countries investing heavily in research and development. The potential applications of quantum life science are vast, ranging from personalized medicine to sustainable energy solutions.
As quantum technologies continue to evolve, their integration into life sciences could lead to transformative changes in how diseases are diagnosed and treated, ultimately improving patient outcomes and enhancing quality of life. The move represents a significant step toward a future where quantum tools are an integral part of healthcare and scientific research.
Meanwhile, the focus on developing human resources and fostering interdisciplinary collaborations will be key to realizing the full potential of quantum life science. As researchers and industry leaders work together, the promise of quantum technologies may soon become a reality, heralding a new era of innovation and discovery.