Microsoft has taken a significant step into the burgeoning field of brain implants by partnering with Inbrain Neuroelectronics, marking the tech giant’s first foray into this innovative space. The collaboration aims to develop advanced therapies for neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and various psychiatric or memory disorders.
The partnership will leverage Microsoft’s agentic AI and cloud technology to enhance Inbrain’s brain-computer interface (BCI), potentially enabling more rapid and responsive treatments based on real-time brain activity. “It’s like upgrading from a remote control to a smart assistant that understands contexts, adapts, and collaborates with you,” explained Carolina Aguilar, CEO and co-founder of Inbrain. She described the system as an “operating system for the body” that continuously interprets brain signals, predicts neural changes, and administers appropriate therapies in real-time.
Innovative Technology and Strategic Collaboration
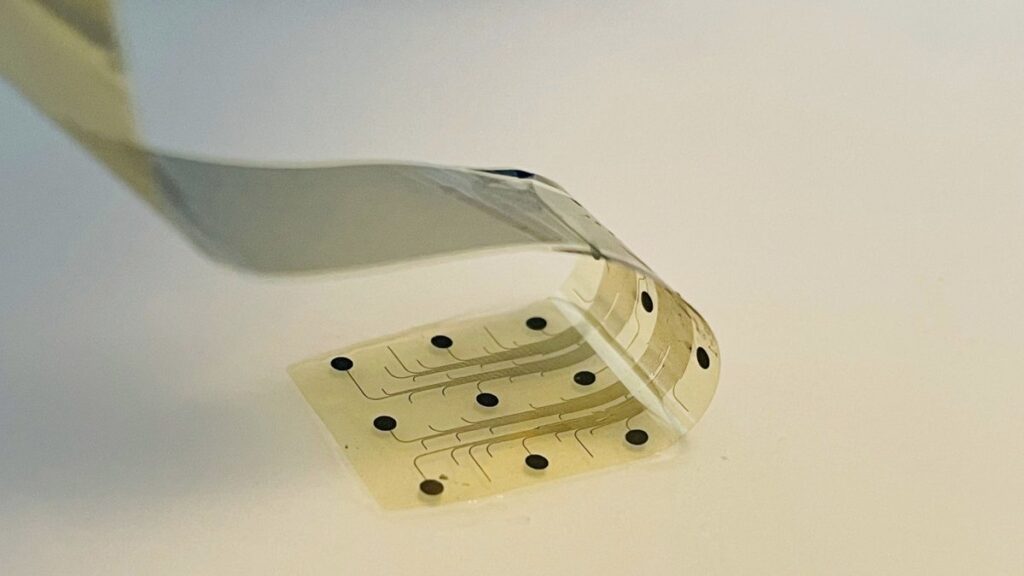
Inbrain’s BCI distinguishes itself from competitors like Neuralink and Synchron by utilizing a unique strap-like design made of graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms. This cutting-edge material offers distinct advantages in terms of flexibility and conductivity. “This collaboration highlights the next frontier of AI,” stated Clare Barclay, Microsoft’s president of enterprise and industry. The decision to collaborate with Microsoft was driven by its robust AI models, secure cloud infrastructure, and extensive experience in regulated healthcare environments.
The initial phase of the partnership focuses on integrating Microsoft’s AI models into Inbrain’s implant to decode brain waves in real-time. Additionally, Inbrain is finalizing the system architecture for clinical applications, with ongoing trials in the UK and plans to expand to the US by 2026. “Instead of bringing people to the neurologist, we aim to bring the neurologist to the people, in real time, in a personalized way, powered by AI and scalable technology,” Aguilar emphasized, highlighting Microsoft’s global reach and data innovation as key enablers of this vision.
Broader Industry Context
Microsoft’s entry into the brain implant sector reflects a growing trend among tech giants exploring this frontier. While Microsoft itself is not manufacturing implants, its involvement mirrors similar moves by Apple, which has developed a standard Bluetooth connection for BCIs, and Synchron, which has begun offering its technology to patients. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman is reportedly raising funds for a brain implant startup called Merge, while Nvidia has been working on digitizing brain waves and applying AI to the data for several years.
Our sources indicate that most tech companies view brain implants as a long-term strategic investment, with current efforts focused on establishing partnerships and observing their evolution over time.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the excitement surrounding these advancements, significant hurdles remain. No brain-computer interfaces have yet received approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and all are at various stages of clinical trials, including Neuralink. The regulatory landscape presents challenges, but the potential for transformative healthcare solutions keeps the industry pushing forward.
The implications of these developments are profound, offering the possibility of personalized, real-time neurological care that could revolutionize treatment paradigms. As Microsoft and Inbrain proceed with their collaboration, the broader tech industry will be watching closely, eager to see how these early partnerships might shape the future of brain-computer interfaces and neurological therapies.
Looking ahead, the success of such initiatives could pave the way for more widespread adoption of brain implants, fundamentally altering how neurological disorders are managed and treated. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to unlock new frontiers in medicine, offering hope to millions affected by debilitating neurological conditions.






